Revised November 6, 2018; June 2, 2019; re-written April 14, 2021; re-written May 7, 2021
“Samphassa” must be used for “phassa” in “phassa paccayā vedanā” in Akusala-Mūla Paṭicca Samuppāda.
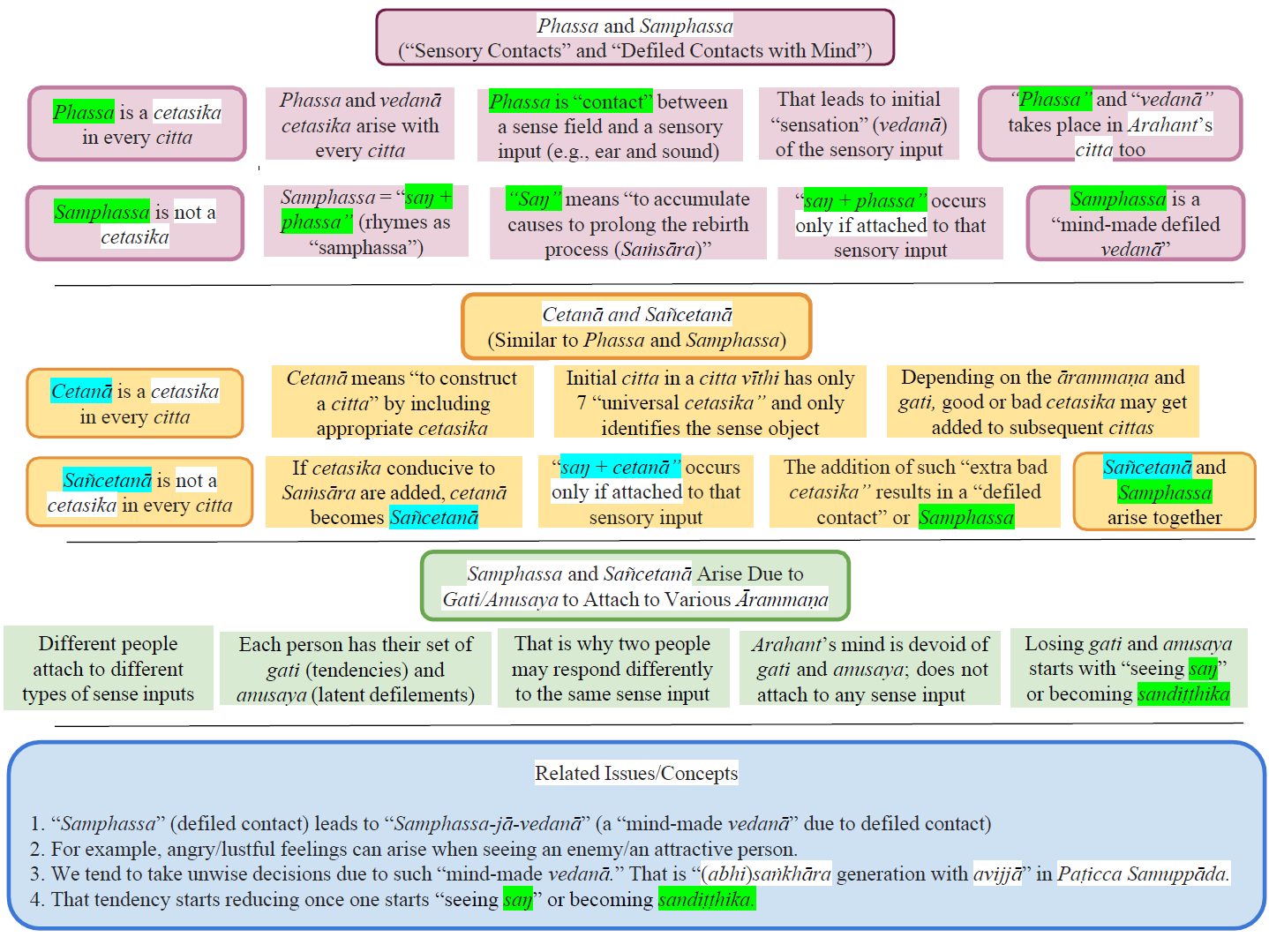
Buddhism – In Charts: 12. Phassa and Samphassa
Download/Print: “WebLink: PDF Download 12. Phassa and Samphassa”
Phassa and Samphassa – Incorrect Translations
1. No differentiation is made between “phassa” and “samphassa” in most English translations of Paṭicca samuppāda. Both words are translated as “contact” in English translations without making the distinction.
▪For example, the “WebLink: suttacentral: Paṭiccasamuppāda Sutta (SN 12.1)” provides the uddesa (utterance) version in Paṭicca samuppāda as “saḷāyatanapaccayā phasso.” The niddesa version of that (brief description) appears in the following “WebLink: suttacentral: Vibhaṅga Sutta (SN 12.2)” as “cakkhusamphasso, sotasamphasso, ghānasamphasso, jivhāsamphasso, kāyasamphasso, manosamphasso.”
▪However, no distinction is made in the translations of the above links. Both are translated as “contact.”
▪As we will see below, “samphassa” has a very different meaning than “phassa” and makes the connection of how our instinctive reactions to external sense experiences arise based on our “saṁsāric habits” or “gati.”
Phassa Is in All Citta
2. When we see, hear, etc. a citta arises that recognize the sensory input. Seven cetasika (mental factors) arise with ANY citta, and phassa and vedanā are two. We will have no sensory experience without the phassa (contact) cetasika.
▪When the mind contacts that image of the external object, a series of citta arises. We experience only the overall effect of millions of such cittā due to that contact.
▪Some of the seven universal mental factors that arise with the citta instantaneously identify the object. These include vedanā and saññā. Both are universal cetasika.
▪If samphassa takes place, there will be an additional, mind-made vedanā called “samphassa-jā-vedanā” as discussed below.
Samphassa – How Does It Arise?
3. An average human will form a like or a dislike for some of the sense inputs (but not for all).
▪If a like or dislike is formed, then that sensory contact is “saŋ phassa” (“saŋ” + “phassa,” where “saŋ” are defilements (greed, anger, ignorance); see, “What is “Saŋ”? Meaning of Sansāra (or Saṁsāra)”). It rhymes as “samphassa.”
▪This “combination effect” or “Pāli sandhi” leads to the pronunciation of many “saŋ” words with an “m” sound: “saŋ” + “mā” to “sammā.” In the same way, “saŋ” “yutta” to “saṁyutta,” “saŋ” “bhava” to “sambhava,” and “saŋ” “sāra” to “saṁsāra”; see, “List of “Saŋ” Words and Other Pāli Roots.” In English texts, “Saŋ” in combined words may be written as Saŋ/San/Saṅ/Saṇ/Sañ/Saṁ/Sam. [See “What is “Saŋ”? Meaning of Saŋsāra (or Saṁsāra)”]
▪Thus, when one sees, hears, smells, tastes, touches something, whether there will be any likes or dislikes towards that sensory experience depends on that person, or more specifically, the “gati” (habits/character) of that person.
Examples of Samphassa
4. Let us discuss some examples to illustrate how “samphassa” arises. First, let us look at the connection with those people/things in the world that we have special relationships with or what we “upādāna,” i.e., like to either keep close or stay away from.
▪Think about the worst “enemy” you have. When you even think about that person X, you generate unpleasant feelings. But X’s family will have loving thoughts about X. Here, you and X’s child (for example) would have generated very different “samphassa” when thinking, seeing, and hearing about X.
▪When you travel by car or bus and look out the window, you may see zillion things, but those are just “seeing”; you don’t pay much attention to them. They are “phassa.” But now, if you happen to see a beautiful house, it piques your interest, and you may even turn back and take another good look at it and even think about how nice it would be to live in a house like that. That is “samphassa.”
5. A critical point is that one’s perception of what is “valuable” can lead to “samphassa.” Suppose someone inherits a valuable gem from his father. Every time he sees it or even thinks about it, he becomes happy. But his mind is also burdened by it since he is worried that he may lose it; he is keeping it in a safe and has put burglar alarms in the house to protect that gem.
▪Suppose one day he asks a professional to evaluate the gem and finds out that it is not a gem but a fake. He may not even believe that initially, but once confirmed, he will become “detached” from it. He will no longer keep it in the safe and may even throw it away in disgust.
▪Now he may be generating neutral or hateful thoughts about the SAME OBJECT he once loved. Nothing changed about the “gem”; it is still the same object as before. What has changed is his PERCEPTION of the value of that object. Whereas he generated “samphassa” on thinking or seeing that object before, now he may generate just “phassa” (neutral feelings) or “samphassa” with quite the opposite feelings of disgust.
Phassa/Samphassa and Cetanā/Sañcetanā
6. Phassa and cetanā are both universal cetasika that arise with every citta. A citta vīthi starts with an “undominated citta” but gets contaminated if the mind gets attached to the ārammaṇa. We do not experience individual cittās but only the cumulative effect of millions of cittās that arise in a second. As cittās get contaminated, asobhana (defiled) cetasika are incorporated by cetanā cetasika it turns into sañcetanā. That happens simultaneously with phassa leading to samphassa.
▪If the “intention” does not involve lobha, dosa, or moha (avijjā), it is only a cetanā or “intention” to get something done. Here, kamma done is just an action without kammic consequences. For example, if one walks to the kitchen to get a glass of water, that is done with a neutral cetanā; the “intention” is to quench the thirst. It is NOT a sañcetanā. There is no “defiled contact” or “samphassa” either.
▪However, almost all current English translations do not make that critical distinction. For example, sañcetanā in the “WebLink: suttacentral: Sañcetanā Sutta (SN 27.7)” is translated as “intention,” and samphassa in the “WebLink: suttacentral: Samphassa Sutta (SN 18.4)” is translated as “contact.” The translators do not understand the difference between Phassa/Samphassa and Cetanā/Sañcetanā.
▪A cetanā becomes a sañcetanā (saŋ + cetanā) — and phassa becomes samphassa — if it involves “saŋ” or lobha, dosa, moha (avijjā.) See “San – A Critical Pāli Root” and “Details of Kamma – Intention, Who Is Affected, Kamma Patha.”
Phassa Can Turn to Samphassa in an Instant
7. Let us take another example that Waharaka Thero gave. This one clearly shows how the transition from “phassa” to “samphassa” can happen very quickly.
The following happened a long time ago in Sri Lanka. A mother had to go overseas when her son was less than a year old. She had been overseas for many years and returned to see her son. She had not even seen any pictures of the boy, who was now a teenager. When she gets home, she is told that the boy is visiting a neighbor, and she starts walking there. On the way, she bumps into a teenager; she admonishes the teenager for not paying attention and resumes walking. But then another person on the street says, “Don’t you recognize your son? Well. How can you? You have been away all this time”. Hearing that, she says, “Oh, is that my son?” and immediately runs back and hugs him.
▪She saw the boy when he bumped into her and even got upset with him. But at that time, he was just a teenager to her. That “seeing” event involved “phassa.”
▪But when someone pointed out that it was her son, her perception of the boy took a giant leap instantly. Now she looks at the same boy with a new set of “mental baggage.” Now it is not just a teenager, but her son; attachment is involved. Now when she looks at him, “samphassa” is involved.
8. We can also see how “samphassa” leads to an intensified vedanā or feelings. This is called “samphassa-jā-vedanā” or “vedanā arising due to samphassa.” This “mind-made defiled vedanā” is different from the universal vedanā as we discussed in #7 above.
▪She had neutral thoughts (may be even some annoyance) when the boy bumped into her and apologized. But when she learned it was her son, her feelings instantly turned to joy.
▪To take it a bit further, if that teenager got hit by a car after several minutes, that joy would turn instantly to sorrow.
▪These different types of “vedanā” arise based on the type and level of “attachment” to a given object, in this case, the boy.
Samphassa/Sañcetanā – Connection to Gati
9. “Samphassa” is intimately connected to one’s “gati” or habits, most of which come from our past lives, even though some may be strengthened or weakened by what we do in this life. We may even start forming new “gati” in this life. Note that “gati” is pronounced “gathi,” like in “Thief.”
▪For example, a young lady looking at a dress may form a liking for it. Another person seeing his enemy will form a dislike. Upon hearing a song, a teenager may form a liking/craving for it, etc.
▪This “contact with saŋ” (or samphassa) happens instantaneously. That initial samphassa arises automatically purely based on our “gati.” But since our actions based on that initial reaction take some time, we still have time to control our speech or bodily actions. Even if bad thoughts come to our minds, we can stop speech or bodily actions. That is Kāyānupassanā in Satipaṭṭhāna meditation or Ānāpānasati.
▪Many posts on this site discuss “gati,” and at the fundamental level, both Ānāpāna and Satipaṭṭhāna meditations are all about removing bad “gati” and cultivating good “gati”; see, “9. Key to Ānāpānasati – How to Change Habits and Character (Gati)”.
An Arahant Has Phassa but Not Samphassa
10. Now, let us consider what happens when an Arahant sees or hears similar things (phassa or “contact” occurs.) He/she will see or hear the same thing as any other person.
▪But an Arahant will not be attracted to it or repelled by it. There will be no samphassa. Thus, there will be no “samphassa jā vedanā” either.
▪Put another way, an Arahant sees, hears, etc., without bias or samphassa. He/she will also generate vedanā, but not “vedanā due to samphassa.”
▪An Arahant has removed all such defiled “gati,” closely related to cravings or “āsava.” An Arahant has removed all “āsava”; this is what is meant by “āsavakkhaya” at the Arahanthood. This is a technical detail that may not be clear to some; don’t worry about it if it unclear yet.
▪Samphassa cannot be removed with willpower. It gradually fades away as one attains higher stages of magga phala (starting with comprehending “saŋ” by becoming “Sandiṭṭhika”; see below.)
Samphassa Leads to Samphassa-jā-Vedanā
11. Therefore, now we can see that the step “phassa paccayā vedanā” in Akusala-Mūla Paṭicca Samuppāda is the “uddesa version” and “samphassa paccayā samphassa-jā-vedanā” is the “niddesa version;” see “Sutta Interpretation – Uddesa, Niddesa, Paṭiniddesa.”
▪However, in most English translations, “phassa paccayā vedanā” in Akusala-Mūla Paṭicca Samuppāda is translated as “Contact is a condition for feeling” (“WebLink: suttacentral: Paṭiccasamuppāda Sutta (SN 12.1)”) and just below that (at the marker 3.6) “phassa nirodhā vedanā nirodho” is translated “When contact ceases, feeling ceases.” after one attains Arahanthood. That INCORRECTLY implies an Arahant would not have feelings! However, an Arahant would have “vedanā” but NOT “samphassa-jā-vedanā.”
▪For an Arahant, there is only “phassa” or mere contact with the external sensory input. An Arahant will thus “see,” “hear,” “smell,” “taste,” or “feel” the same things as any other person. But an Arahant will not be attached or repulsed by that sensory experience.
▪I have discussed many problems with translators directly translating the “uddesa versions” of key verses; see “Word-for-Word Translation of the Tipiṭaka.”
▪More details on how “samphassa” leads to samphassa-jā-vedanā at: “Vedanā (Feelings) Arise in Two Ways,” “Vipāka Vedanā and “Samphassa jā Vedanā” in a Sensory Event,” and “Dukkha Samudaya Starts With Samphassa-Jā-Vedanā.”
Samphassa-jā-Vedanā Starts to Fade Away When One Becomes “Sandiṭṭhika”
12. The defiled contacts (“samphassa”) (and also defiled intentions or sañcetanā) start fading away when one becomes a Sotāpanna Anugāmi.
▪That happens when one starts comprehending the Noble Truths/Paṭicca Samuppāda/Tilakkhaṇa or “seeing saŋ” or “sandiṭṭhika” (saŋ diṭṭhi.)
▪All posts in the new section on “Buddhism – In Charts.”
Next, “Phassa Paccayā Vedanā….to Taṇhā”, ……….